Precision machined parts are made to fit exactly with other parts. Makers use special machines like CNC milling, turning, and grinding. These machines help them make parts that are very accurate. These parts are important in many industries like cars, medicine, and airplanes. In 2023, car makers needed precision machined parts for engines and transmissions. KEMING uses a special way that mixes metal investment casting with precision machining. This helps them make parts that are very high quality.
Key Takeaways About Precision Machined Components Overview
Precision machined parts are made to fit with other parts. This makes sure they are very accurate and high quality. These parts are used in cars, planes, and medical tools.
Tolerances in precision machining are very small. In medical devices, they can be as tiny as 1-3 microns. This helps stop breakdowns and makes products work better.
Surface finish changes how parts move and wear out. Smoother finishes lower friction and help parts last longer.
CNC machining and casting are important ways to make precision machined parts. These methods let us create complex shapes and smooth finishes.
Picking the right materials, like metals or plastics, is very important. It helps the parts last longer and work well.
Precision Machined Features
Tolerances in Precision Machining for Exact Dimensions
Tolerances show how much a part’s size can change. The part still works if it stays in these limits. Engineers set these limits for each part. This makes sure every piece fits and works right. In precision machined parts, tolerances are very small. Most CNC shops use a standard tolerance of +/- 0.005 inches (0.13 mm). Some industries need even smaller tolerances. Medical device makers want tolerances as tiny as 1-3 microns. Aerospace companies may need parts with tolerances of 2 microns or less.
L'industrie | Typical Tolerance Range |
|---|---|
General Machining | +/- 2-5 thousandths of an inch |
Fabrication de dispositifs médicaux | 1-3 microns |
Aérospatiale | 2 microns or less |
Usinage CNC | +/- 0.005 inches (0.13 mm) |
CNC Micro Machining EDM | +/- 0.010mm to +/- 0.025mm |
CNC Fiber Laser Machining | +/- 0.0127mm to +/- 0.0254mm |
CNC Femto Laser Machining | +/- 0.001mm to +/- 0.010mm |
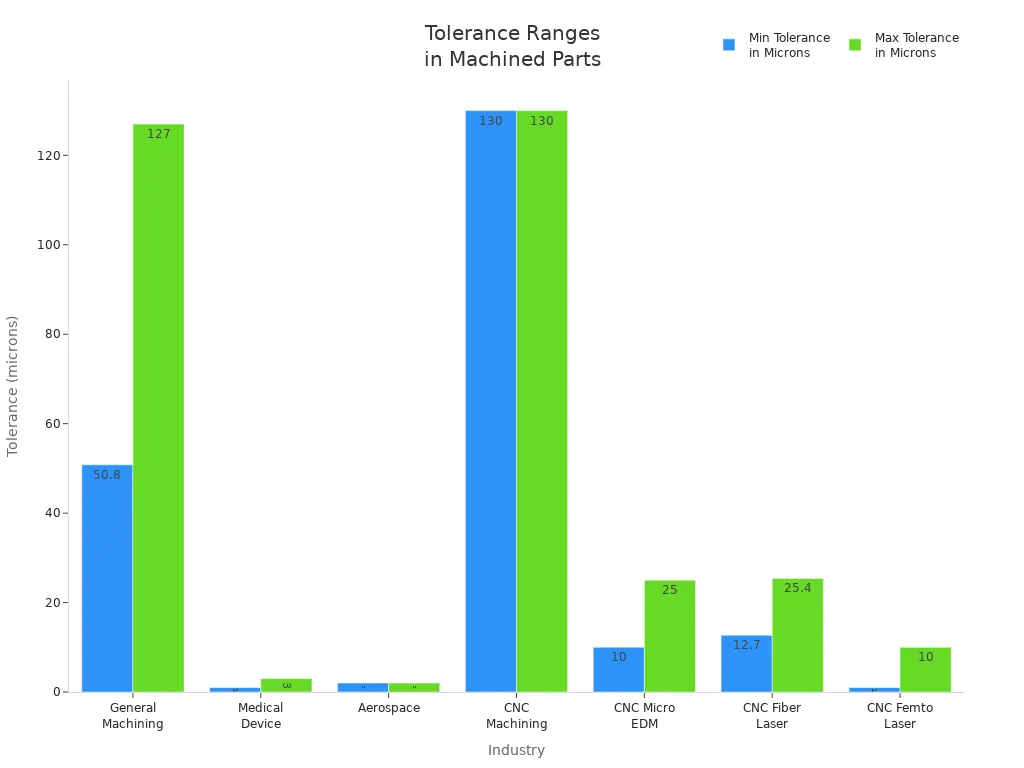
Small tolerances help parts fit together well. This lowers the chance of breakdowns. It also makes products better. Even tiny mistakes in tolerance can cause big problems. This is true for cars and airplanes. KEMING uses advanced machines to keep tolerances tight and steady.
Accuracy Levels Achieved in Precision Machined Parts
Accuracy means how close a part’s size and shape are to the design. Precision machined parts must match the design exactly. Workers use special tools to check accuracy. These tools include coordinate measuring machines, optical comparators, and precision gauges. Laser scanning and automated systems also help measure parts fast and correctly.
Tolerance Range | Exemples d'application | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
±0.0025 mm (±0.0001″) | Surgical instruments, precision bearings | Medical devices, aerospace |
±0.0076 mm (±0.0003″) | Hydraulic components, optical mounts | Defense, instrumentation |
±0.0127 mm (±0.0005″) | Connector housings, valve bodies | Automotive, electronics |
±0.0254 mm (±0.001″) | Structural components, housings | General precision manufacturing |
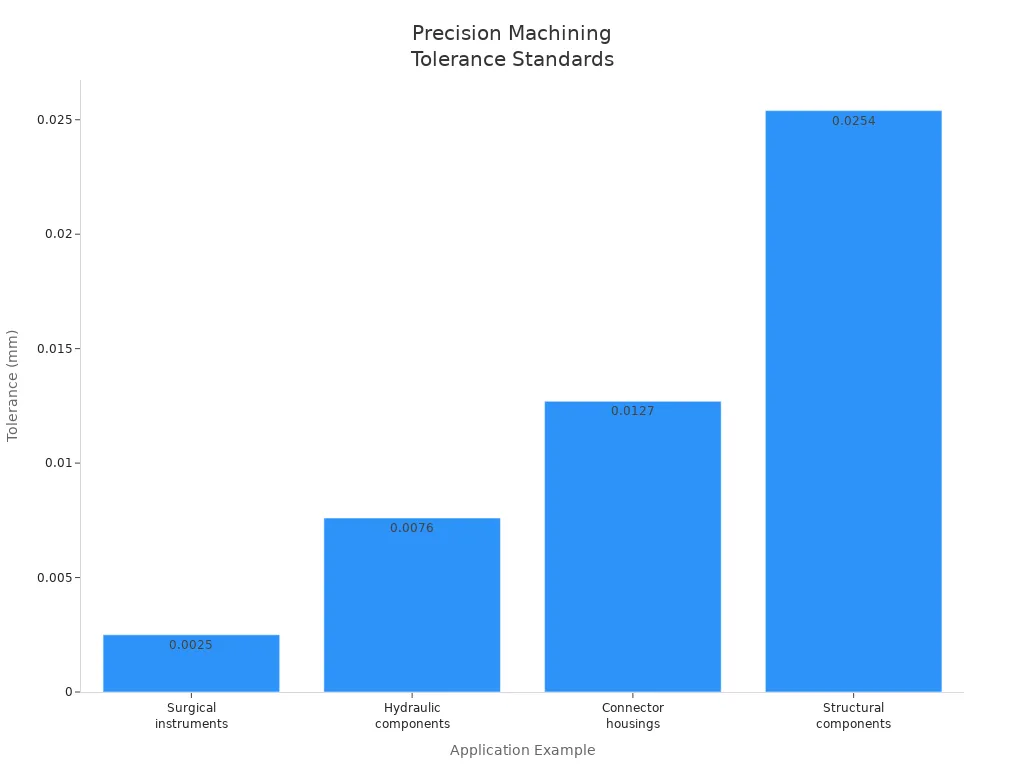
Quality checks happen all the time. First article inspection checks the first part made. In-process monitoring watches parts as they are made. Statistical process control helps find problems early. Certification standards like ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100D make sure parts follow strict rules. KEMING uses these methods to give customers precision machined parts that meet their needs.
Surface Finish Quality of Precision Machined Components
Surface finish tells how smooth or rough a part feels and looks. The finish affects how parts move, wear, and seal. Engineers measure surface finish using Ra values. Ra values show the average roughness in micrometers (µm). Smoother finishes help parts last longer and work better.
Surface Finish Grade | Ra Value (µm) | Caractéristiques | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
RGN 3.2 | 3.2 | Moderately rough surface | Common in less critical parts like general hardware and construction components. |
RGN 6.3 | 6.3 | Rougher surface texture, visible to the naked eye | Suitable for less refined applications like certain industrial equipment and consumer products. |
RGN 12.5 | 12.5 | Clearly rough surface | Often found in components that require increased friction or grip. |
RGN 25 | 25 | Very rough surface | Used in applications where surface finish is not critical, such as in some castings and rough forgings. |
RGN 50 to RGN 800 | 50 to 800 | Progressively coarser surfaces | Cater to very rough and coarse applications, often in heavy machinery, agricultural equipment, and non-aesthetic components. |
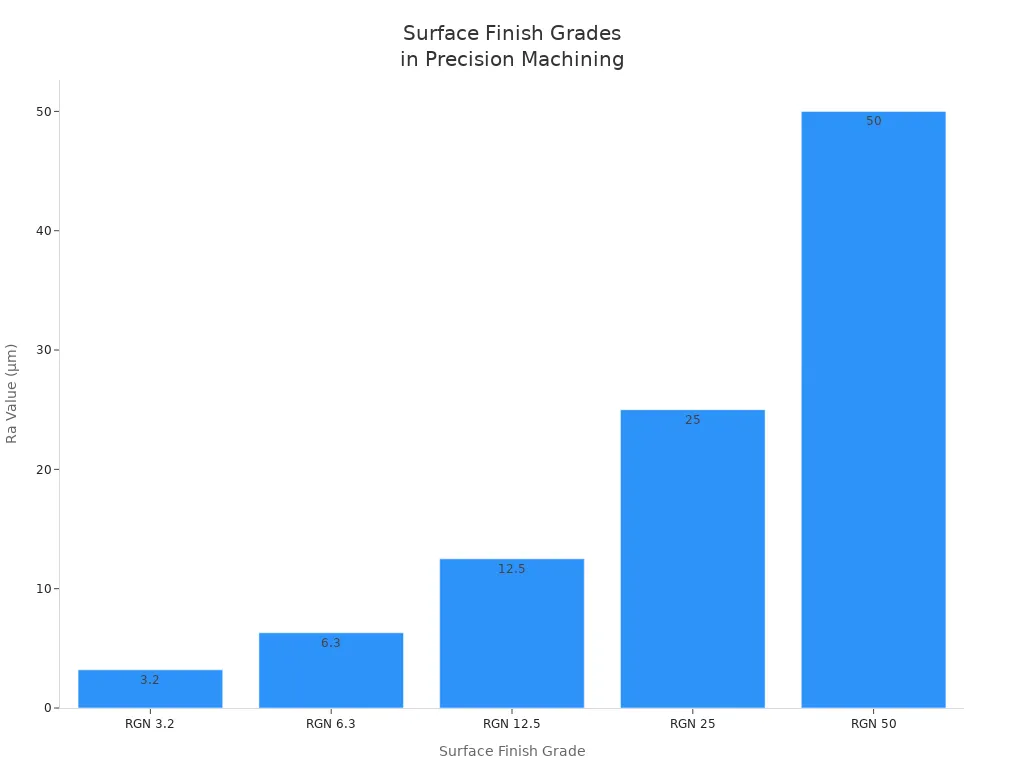
Surface finish matters for many reasons:
Smoother surfaces lower friction and wear.
Good finishes help seals work better.
Shiny finishes look nice and can help electricity flow.
Rough surfaces help paint and glue stick.
In a ball bearing, a smooth surface finish lowers friction. This helps the bearing last longer. If the finish is poor, the bearing may wear out fast. This can happen even if its size is correct.
KEMING uses contact and non-contact ways to measure surface finish. Machine vision and ultrasonic sensors help check finishes during production. Their hybrid process mixes casting and CNC machining. This makes parts with great surface finishes and tight tolerances.
Manufacturing Processes Used for Precision Machined Parts

KEMING uses many advanced ways to make precision machined parts. Each way helps shape, improve, and finish parts. These parts are needed in industries that want high accuracy.
CNC Machining Process for High Precision Manufacturing
CNC machining means Computer Numerical Control machining. This way uses computers to control machines. The machines cut, shape, and finish metal or plastic parts. They follow exact plans from a digital design. This makes parts with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
Main steps in CNC machining:
Define: Engineers choose what the part does and how it looks.
Feasibility: They check if machines can make the part.
Develop: Designers and makers build digital models with CAD or CAM.
Validate: Each part gets checked to match the design.
Implement: The CNC machine makes the part.
Evaluate: Teams test the part and look for ways to make it better.
CNC machining has many good points:
It makes parts with high precision and tight tolerances.
Machines can work for a long time with little help.
The process lowers mistakes and waste by using less human work.
KEMING uses CNC milling, turning, drilling, and EDM to make complex shapes. Their shop has more than 50 CNC machines. This helps them fill both small and big orders.
Casting Techniques Combined with Precision Machining Processes
Casting shapes metal by pouring it into a mold. KEMING uses metal investment casting to make the main shape of a part. First, they make a wax pattern and cover it with ceramic. When the ceramic hardens, the wax melts away. This leaves a space for metal. Hot metal fills the space and cools to make the part.
Investment casting makes parts with lots of detail and accuracy. It works well for parts that need to be strong or fight rust. This way is great for making tough, high-quality parts.
Processus | Tolerances Achievable |
|---|---|
Usinage CNC | Up to +/- 0.0002” (0.005 mm) |
Casting | Generally looser tolerances |
CNC machining gives smoother surfaces than casting. Casting leaves rougher surfaces. KEMING uses CNC machining to make cast parts more accurate and smooth.
KEMING’s special way starts with investment casting and ends with CNC machining. This mixes the best parts of both ways. It makes precision machined parts with great detail and surface quality.
Grinding Operations for Enhanced Surface Quality and Fit
Grinding is a finishing way that makes parts more accurate and smooth. KEMING uses CNC grinding to meet strict rules for flatness, parallelism, and smoothness.
Common grinding methods include:
Surface Grinding: Makes flat surfaces smooth and exact.
Cylindrical Grinding: Shapes and finishes round surfaces.
Centerless Grinding: Refines small round parts without holding them.
Jig Grinding: Makes complex shapes with high accuracy.
Creep Feed Grinding: Works with tough materials and tricky designs.
Thread Grinding: Makes exact threads for screws and bolts.
Grinding helps parts fit together better and last longer. It can make shiny finishes for low friction and nice looks. Grinding also removes sharp edges to make parts safer.
Grinding is needed for aerospace fasteners, medical devices, and bearing surfaces. It helps precision machined parts meet top standards for quality and reliability.
Quality Control and Customization
KEMING uses advanced tools to check every part. They use CMMs for exact measurements. Optical comparators find defects. Surface testers check smoothness. Hardness testers check material strength. Non-destructive tests like ultrasonic and X-ray look for hidden problems.
KEMING changes its ways to fit each client’s needs. They pick the best materials, design parts with CAD, and choose the right machining ways. Their skill and technology help them give precision machined parts that match what customers want.
Materials Commonly Used in Precision Machined Components
Metals Materials for Precision Machined Industrial Parts
Metals are used a lot for precision machined parts. They are strong and last a long time. Engineers pick metals based on what the part needs to do. Some common metals are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, titanium, alloy steel, cast iron, and magnesium. Each metal has its own special traits for different uses.
Métal | Propriétés |
|---|---|
Aluminium | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, easy to machine, cost-effective |
Acier inoxydable | Excellent strength, corrosion resistance |
Laiton | Good machinability, smooth finish, holds tolerances well |
Titane | High strength-to-weight ratio, resistant to oxidation and heat |
Acier allié | Strong, durable, suitable for many applications |
Fonte | Good wear resistance, machinability |
Magnésium | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio |
The metal you pick changes how easy it is to machine. Hard metals can wear out tools faster and need slow cutting. Softer metals are easier to cut but need careful work to stay accurate. Surface treatments like anodizing and plating help stop rust and make metals harder.
Engineers think about design, rules, and standards when picking metals. The right metal helps parts last longer and work better.
Plastics Materials for Lightweight Precision Machined Components
Plastics are important in precision machining. They are good for parts that must be light or resist chemicals. Some plastics used are ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (PE), polyetheretherketone (PEEK), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyamide (PA), and polyacetal (POM). These plastics are tough and safe for things like medical and food parts.
Propriété | Métaux | Plastiques |
|---|---|---|
Strength and Hardness | High strength and hardness | Low strength and hardness |
Machining Speed | Difficile à usiner | Des vitesses d'usinage plus rapides |
Usure des outils | Usure rapide de l'outil | Moins d'usure des outils |
Poids | Poids élevé | Poids léger |
Résistance à la corrosion | Mauvaise résistance à la corrosion | Bonne résistance à la corrosion |
Qualité de surface | Excellente qualité de surface | Sensible aux rayures et aux bavures |
Résistance à la température | Bonne résistance aux températures élevées | Mauvaise résistance à la température |
Les plastiques coûtent moins cher que les métaux et sont plus légers à expédier.
Ils ne nécessitent pas de finition supplémentaire et résistent aux produits chimiques.
Les plastiques peuvent être usinés plus rapidement et n'usent pas autant les outils.
Les ingénieurs utilisent les plastiques pour les pièces qui doivent être sûres, légères et faciles à nettoyer. Ces matériaux permettent de respecter les règles de conception et de sécurité dans de nombreux domaines.
Applications usinées avec précision

Utilisations industrielles de l'usinage de précision dans la fabrication
Precision machined parts sont importantes dans de nombreux domaines. Ces domaines ont besoin de pièces exactes, solides et sûres. Parmi les plus grands utilisateurs, on peut citer
Aérospatiale: Nécessite des pièces très précises pour les moteurs et le train d'atterrissage.
Automobile: utilise ces pièces dans les moteurs, les transmissions et les systèmes de sécurité.
Dispositifs médicaux: Nécessite de petites limites pour les outils et les implants.
Électronique: Nécessite des pièces minuscules et détaillées pour les circuits imprimés et les connecteurs.
Défense: Besoin de pièces métalliques solides et précises pour les armes et les véhicules.
Pétrole et gaz: Utilise des pièces résistantes pour les pompes et les vannes dans des endroits difficiles d'accès.
L'énergie: A besoin de pièces qui fonctionnent bien dans les turbines et les systèmes d'alimentation.
Transformation des aliments: Besoin de pièces sûres et faciles à nettoyer pour les machines.
Le marché de l'usinage de précision connaît une croissance rapide. En 2024, il représentait environ 114,58 milliards de dollars. Les experts pensent qu'il doublera d'ici 2033, car de plus en plus de domaines ont besoin de pièces de qualité.
Exemples de composants usinés de précision couramment utilisés
L'usinage de précision permet de fabriquer de nombreux types de pièces. Ces pièces doivent être bien ajustées et fonctionner dans des conditions difficiles. En voici quelques exemples :
Type de composant | L'industrie | Description |
|---|---|---|
Engrenages | Automobile | De bons engrenages facilitent la transmission de la puissance |
Composants de la transmission | Automobile/Aérospatiale | Nécessaire pour les voitures et les avions électriques |
Composants aérospatiaux | Aérospatiale | Fabriqué avec des machines CNC pour une grande précision |
Composants du moteur | Automobile | Découpe au laser pour un meilleur travail et une plus grande confiance |
Dispositifs médicaux | Médical | Outils et implants à petites limites |
Composants de la batterie | Électronique | Des pièces minuscules et détaillées pour stocker l'énergie |
Systèmes d'éclairage | Automobile/électronique | Pièces sur mesure pour les nouveaux systèmes d'éclairage |
KEMING fabrique ces pièces à l'aide de machines CNC et de moulages de pointe. L'équipe suit des règles strictes en matière de précision et de finition.
Avantages des pièces usinées de précision dans la production
Precision machined parts apportent beaucoup de bonnes choses aux fabricants et aux utilisateurs :
Une grande précision permet aux produits de mieux fonctionner et d'être plus sûrs.
Les petites limites permettent de s'assurer que les pièces s'adaptent et fonctionnent correctement.
L'usinage CNC permet de réduire les déchets et d'économiser les matériaux.
Les machines réduisent les risques de blessures au travail.
Les pièces sur mesure permettent de répondre à des formes et à des besoins particuliers.
Good parts mean less downtime and fewer repairs.
KEMING’s special process gives parts with top quality and steady results. Their skill helps clients in tough fields like aerospace and medical devices get the best outcomes.
Precision machined parts are important in many industries. They help machines work well and last longer. Companies use these parts to follow safety rules. This lowers the chance of things breaking.
Precision machining makes systems work better in aerospace and other areas.
Strong parts break less often and help keep people safe.
Saving money happens because there is less waste and fewer fixes.
Custom designs let engineers make new ideas.
KEMING gives top-quality parts using advanced tools. Makers who pick precision machining get better products and stronger results.
FAQ
What does “precision machined part” mean?
A precision machined part is made with exact sizes. Machines shape it so it fits with other parts. These parts help products work well and last longer.
Why do industries need tight tolerances?
Tight tolerances make sure parts fit with no gaps. This helps machines work smoothly. Aerospace and medical fields need tight tolerances for safety.
Which materials work best for precision machining?
Metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium work well. Plastics like PEEK and ABS are also used. Engineers pick materials for strength, weight, and use.
Tip: Picking the right material helps the part last longer and work better.
How does KEMING ensure quality in every part?
KEMING uses advanced machines and strict checks. Workers measure each part with special tools. They follow rules to make sure each piece meets needs.
Can precision machined parts be customized?
Yes, engineers can design parts for special jobs. KEMING offers custom shapes, sizes, and finishes. This helps clients get what they need for their projects.




