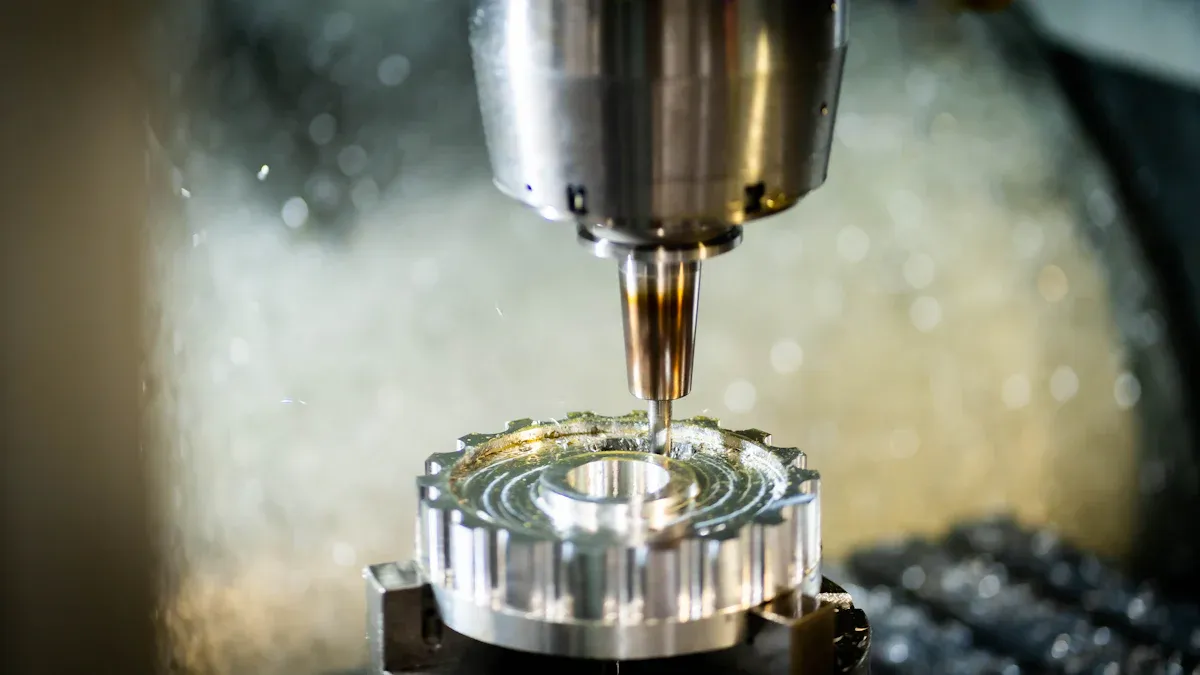
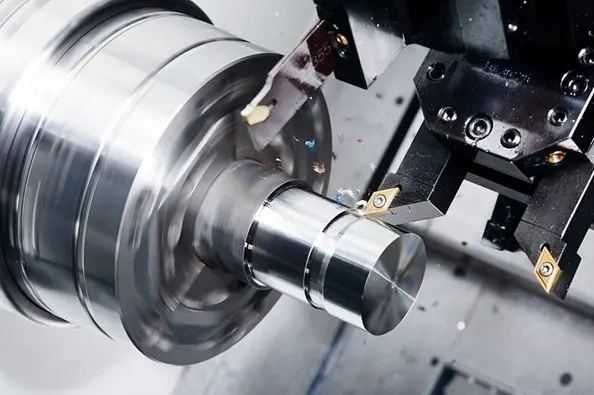
CNC-Drehen is a process that transforms raw materials into precise, circular parts. Most people understand CNC turning as a method of manufacturing precision parts using a computer-controlled lathe. This subtractive manufacturing process removes material from a workpiece using an automatically operated machine tool. Many industries use CNC turning due to its high accuracy and consistency. KEMING is a trusted provider of CNC turning and precision casting services.
Wichtigste Erkenntnisse
- CNC turning transforms raw materials into precise, circular parts. It uses a computer-controlled lathe. The process involves several steps, including design, material selection, machining, and part inspection. These steps ensure the quality and accuracy of the parts. CNC turning is ideal for automotive and aircraft manufacturing companies and can be used to produce parts such as shafts, bushings, and connectors. Using high-quality materials, such as metals and plastics, can improve the performance and lifespan of the parts. CNC turning is fast and consistent, making it a cost-effective method for high-volume part production.
CNC Turning Process Overview
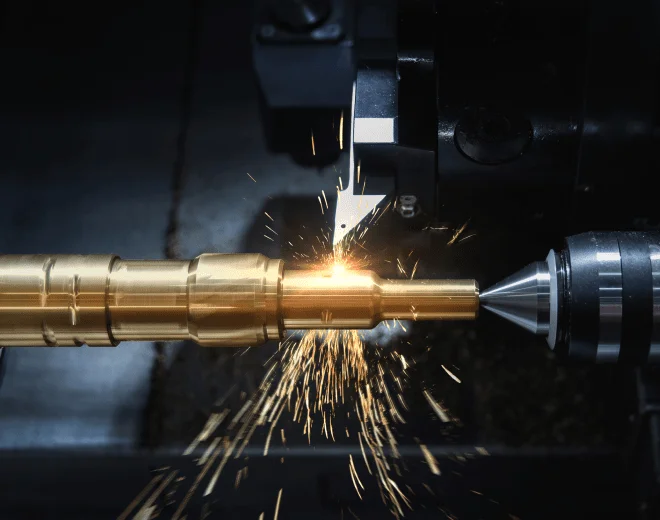

How CNC Turning Works
The CNC turning process uses a computer-controlled lathe. The machine clamps a solid workpiece and rotates it at high speed. A cutting tool moves across the surface of the workpiece and removes material. Because the process removes material, it is called subtractive manufacturing. This process generates chips and waste material but allows for high precision and repeatability.
Operators program the CNC lathe using G-code. The program instructs the machine on the rotational speed and the position of the cutting tool, and controls tool changes. Automation helps reduce errors and ensures that each part has the same appearance. The CNC system can save programs, allowing factories to produce the same parts multiple times.
KEMING uses modern CNC machines to ensure precise and consistent machining results. Their employees follow safety regulations, such as wearing protective gear and inspecting the machines before operation. They maintain a clean work area and use safety guards to ensure personnel safety.
Tip: Computer numerical control systems help manufacturers achieve tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, making CNC turning ideal for industries that require reliable parts.
CNC turning Basic Steps in the Process
The CNC turning process involves several steps to produce a finished part. Each step builds upon the previous one to ensure quality and accuracy.
- Design and Programming: Engineers design the part using CAD software. They convert the design into CNC programs used to control the machine tools.
- Material Selection: The team selects the best materials based on the part’s application. They typically use metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and iron.
- Machine Setup: Operators load the raw material into the lathe and set the cutting tools. They check that all components are aligned and prepare the machine.
- Rough Machining: The machine removes a large amount of material to form the basic shape.
- Finishing: More precise tools give the part its final dimensions and a smooth surface. This step ensures accurate part dimensions.
- Inspection: Workers measure and inspect the parts to ensure they meet design requirements.
- Post-processing: Some parts require additional steps before use, such as cleaning or coating.
KEMING’s technological advantages in CNC turning and precision casting enable them to produce parts that meet international standards. Their production process employs meticulous planning, precise machining, and rigorous inspection to ensure product quality.
Note: Each step in the CNC turning process is crucial for manufacturing robust, durable, and high-quality parts for industries such as automotive, construction, and mining.
CNC Turning Operations & Machines
Common Turning Operations
CNC turning uses different steps to shape parts. Each step has its unique function. These steps help in manufacturing parts with the correct dimensions. Operators select the best machining steps for each part.
- Facing: The tool moves across the end face of the part. This flattens the end face and shortens the part length. Facing ensures the end face is at a right angle.
- Turning: The tool cuts along the side of the part. This creates straight, tapered, or curved shapes. Turning is used for machining shaft-like parts, etc.
- Grooving: The tool cuts a narrow groove in the part. Grooving allows control over the depth and width of the groove. This is suitable for parts like O-rings.
- Thread Cutting: The tool moves laterally while the part rotates. This creates a helical groove called a thread. Thread cutting is necessary for threaded fasteners.
- Boring: The tool enlarges a hole inside the part. Boring helps in achieving the correct hole diameter.
- Drilling: The tool drills a hole in the center of the part. Drilling is used for engine blocks and other parts.
- Knurling: The tool presses a pattern onto the outer surface of the part. Knurling helps improve the grip of the part and gives it an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Tapping: A cutting tool is used to machine threads inside a hole. Tapping is used in mechanical and electronic equipment.
Tip: CNC turning can make parts very exact, about ±0.005″ (0.13 mm). If needed, workers can make parts even more exact.
| Operation | Beschreibung | Features | Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Einfädeln | Cutting helical grooves on cylindrical parts. | Internal or external threads; various shapes. | Used for fasteners and connectors. |
| Tapping | Machining threads inside a hole. | Precise thread dimensions; suitable for various materials. | Used in mechanical and electronic equipment. |
| Turning | Cutting material to form a circular shape. | Can be straight, tapered, or curved shapes. | Used for shafts and bushings. |
| Facing | Cutting the end face to create a flat surface. | Bringing the part to the correct length. | Used for flanges and gears. |
| Boring | Enlarging a hole or cavity. | Provides precise hole dimensions. | Used for engine parts. |
| Bohren | Drilling a hole at a central location. | Hole sizes can vary. | Used for engine blocks, etc. |
| Nuten | Cutting fine lines on a surface. | Controls the depth and width of the lines. | Used for seals and hydraulic parts. |
| Rändeln | Creating a rough pattern on an external surface. | Can be cross-hatched or diagonal lines. | Used to increase grip and for aesthetics. |
CNC Lathes and Tooling
CNC lathes are essential for turning operations. These machines hold and rotate the part. Cutting tools shape the part as it rotates. Different types of CNC lathes are used for different machining tasks.
- Horizontal CNC lathes are used for turning and boring. Many factories use them.
- Vertical CNC lathes hold the part vertically. They are suitable for large or irregularly shaped parts.
- Horizontal turning centers can perform turning, milling, and drilling. They use multiple tools and axes for complex machining.
- Vertical turning centers combine the functions of other machines.
Operators use specialized tools to create higher-quality parts. Tool types include grooving tools, cutoff tools, knurling tools, threading tools, straight turning tools, facing tools, drills, boring tools, and taper turning tools. Each tool helps ensure that the same part is produced every time.
KEMING uses new CNC machines and modern tools. Their machines produce parts with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces. Skilled workers select the best tools for each job. This ensures that every part is manufactured correctly.
Note: Using the right CNC lathe and tools can help companies obtain strong and durable precision parts for automotive, construction, and electronic products.
CNC Turning Materials
Metals for CNC Turning
Many companies use metals for CNC turning. Metals are strong and durable. Some common metals include carbon steel, stainless steel, iron, aluminum, brass, copper, and special alloys such as titanium. Each metal is best suited for specific applications.
| Metall | Vorteile |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | Sharp cutting edges, lightweight, and fast machining speed. Coolant helps prevent chip adhesion. |
| Low/Medium Carbon Steel | Requires strong tools and tool holders. Slower cutting speed, but high strength. |
| Rostfreier Stahl | Requires high-temperature resistant inserts. Coatings help reduce friction. Cooling is crucial. |
| Brass and Copper | Sharp cutting edges and bright surface finish. Chips are easy to control. |
| Exotic alloys (e.g., titanium) | Requires special high-temperature resistant inserts. Strict cooling requirements. Slow cutting speed and requires strong tools. |
KEMING specializes in CNC turning of carbon steel, stainless steel, and iron. Carbon steel is hard and strong, suitable for parts requiring durability. Stainless steel has good toughness, is less prone to breakage, and can withstand impact, making it suitable for frequently used parts. Iron is strong and easy to form, used in the manufacture of many mechanical parts. KEMING also processes aluminum and other alloys. These materials are lightweight and resistant to rust.
Tip: Choosing the right metal helps create high-performance parts, such as car engines or building frames.
Plastics and Other Materials
CNC turning can also process plastics and other materials. Plastics are softer and easier to cut. However, overheating can occur if not careful. Plastics
| Plastic | Wichtige Eigenschaften | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Strong and tough | Used for housings and brackets |
| FR4 | Hard and heat-resistant | Used for circuit boards |
| Nylon (PA6) | Wear-resistant and smooth | Used for gears and moving parts |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | High strength and transparent | Used for protective covers and shields |
| PMMA (Acrylic) | Transparent and lightweight | Used for displays and lighting equipment |
| POM (Delrin/Acetal) | Dimensionally stable and smooth surface | Used for bearings and valves |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Smooth and chemically resistant | Used for seals and gaskets |
| Bakelite | Hard and heat-proof | Used for electrical components |
Plastics such as ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate are widely used. They are suitable for electronic products, automobiles, and mechanical equipment. Plastic chips are longer, and less power is required for cutting. However, they may warp if the machine overheats.
| Merkmal | Metalle | Kunststoffe |
|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness | Metals are hard and require robust tools. | Plastics are soft and easy to cut. |
| Chip Formation | Metals make sharp chips. Be careful. | Plastics make long chips. Easy to handle. |
| Heat Generation | Metals get hot and need cooling. | Plastics do not get as hot but can bend. |
| Material Removal Rates | Metals cut slow and need strong machines. | Plastics cut fast but can get too hot. |
CNC turning technology can be used to machine metals and plastics, making it widely applicable. KEMING helps customers select the most suitable materials for their needs.
CNC Turning vs CNC Milling
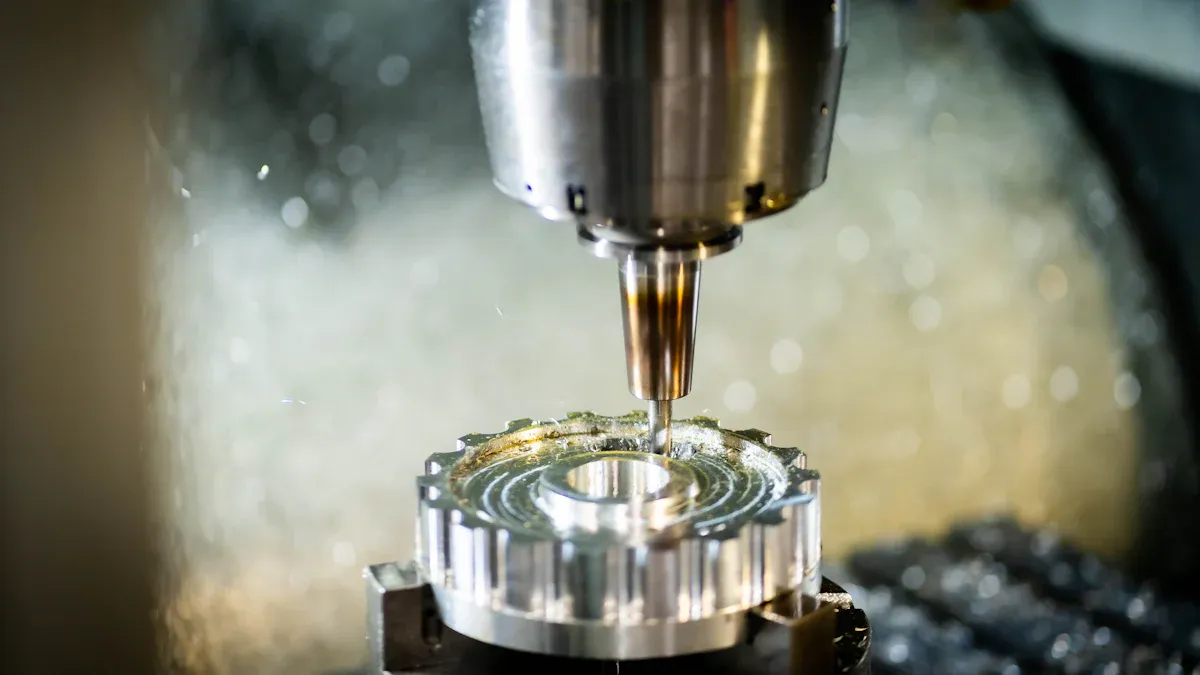

Wesentliche Unterschiede
Both CNC turning and CNC milling are methods of shaping parts, but they work differently. In CNC turning, the machine rotates the workpiece at high speed, and the cutting tool removes material as the workpiece rotates. In CNC milling, the workpiece remains stationary, and the cutting tool moves around the workpiece to perform the cutting.
The table below lists their main differences:
| Aspekt | CNC-Drehen | CNC-Fräsen |
|---|---|---|
| Workpiece Movement | Workpiece rotates, cutting tool remains stationary. | Workpiece remains stationary, cutting tool moves. |
| Cutting Tools | Uses single-point cutting tools to machine cylindrical parts. | Uses multi-point cutting tools to perform various machining tasks. |
| Machining Complexity | Best suited for symmetrical parts; limited ability to machine complex shapes. | Capable of creating complex patterns and three-dimensional shapes. |
| Number of Axes | Typically 2 axes (X and Z); some machines have more axes for powered tooling. | Typically 3 axes; advanced models can have 5 axes. |
| Produktionsgeschwindigkeit | Faster for machining cylindrical parts due to continuous cutting. | Slower for machining complex patterns, but versatile due to the ability to use multiple tools. |
CNC turning is suitable for manufacturing round parts such as shafts, bushings, and rings. This method can achieve smooth surfaces and maintain the roundness of the parts. CNC milling is used for machining flat surfaces, grooves, and complex shapes. It can manufacture parts with multiple sides and angles.
Tip: CNC turning is best suited for round or tubular parts. CNC milling is better suited for parts with multiple sides or irregular shapes.
Wann sind sie zu verwenden?
CNC turning is used when round or tubular parts are needed. Many industries use this method. Automotive manufacturers use turning to machine axles, pins, and pistons. Aircraft companies use it to machine fittings and landing gear shafts. Medical device manufacturers use turning to machine bone screws and implants. Machines require rollers and bushings manufactured through turning. Here are some examples of applications using CNC turning:
- Automotive: Axles, pins, pistons, threaded fasteners
- Aerospace: Hydraulic fittings, landing gear shafts, couplings
- Medical: Surgical implants, bone screws, dental parts
- Industrial machinery: Rollers, bushings, custom shafts
The table below shows how turning is used in different industries:
| Industrie | Beschreibung der Anwendung |
|---|---|
| Luft- und Raumfahrt | High-quality gears and rotating parts are manufactured using CNC turning. |
| Medical Equipment | Precision turning of steel and other materials is required. |
| Automobilindustrie | Turning is used to machine parts with precise cuts and smooth surfaces. |
KEMING Company uses CNC turning to manufacture robust circular parts for automobiles, aircraft, and machinery. Their team selects the best method for each job. CNC turning is suitable for the rapid machining of circular parts. CNC milling is more suitable for machining flat or complex-shaped parts.
Note: Choosing the right method helps companies obtain the best parts to meet their needs.
CNC Turning Advantages & Disadvantages
Benefits of CNC Turning
CNC turning technology offers numerous benefits to modern factories. Businesses favor CNC turning because of its speed and ability to produce highly precise parts. It can also repeatedly produce identical parts without error. Here are some of the main advantages of CNC turning:
- CNC machines are faster than manual work using hand tools.
- Automation helps reduce errors and ensures part quality.
- The process can produce highly precise parts, even with complex shapes.
- Every part in a batch is identical to the first one.
- CNC turning allows workers to quickly change designs and use new tools quickly.
The table below shows the differences between CNC turning and manual turning:
| Vorteil | CNC-Drehen | Manual Turning |
|---|---|---|
| Genauigkeit | Excellent accuracy and repeatability | Limited precision |
| Wirkungsgrad | High efficiency due to automation capabilities | Slower speed, requires manual operation |
| Repeatability | Consistent quality in large-scale production | Quality fluctuations |
CNC technology also helps produce parts faster. Automation means less manual labor, leading to increased production speed. Specialized software helps plan tool paths and check them before cutting begins. This allows businesses to deliver parts faster and fulfill large orders.
KEMING utilizes strict quality control and advanced CNC machines. Their team inspects every part to ensure it is durable and meets requirements. Customers receive high-quality service and parts that meet their needs.
Tip: CNC turning is ideal for companies that require large quantities of durable, high-quality parts.
Limitations and Challenges
CNC turning also has some limitations. It is best suited for round parts or parts that rotate around a central axis. It cannot process non-circular shapes. Equipment setup and tooling costs can be high, especially for small-batch production.
Some problems may arise when machining complex parts. Thin-walled parts may bend or break during the turning process. It is difficult to guarantee that every part is perfect in large-scale production. Hard metals like titanium can quickly wear down cutting tools. Parts that need to fit with other components require additional inspection.
KEMING addresses these challenges by utilizing intelligent software and experienced technicians. They adjust cutting methods and use specialized tools based on different machining tasks. Their team collaborates with clients to find the optimal machining solution for each part.
Note: Understanding the advantages and limitations of CNC turning helps businesses choose the best manufacturing method for their parts.
CNC turning uses computer control to machine round parts with high precision. Many businesses choose this method because it is fast and accurate. Companies use CNC turning for mass production of parts, which helps save costs and ensures part quality.
- CNC turning is suitable for metals, plastics, and other materials.
- This process is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
- Machining more parts at once saves time and money.
Quality control is crucial. KEMING has advanced equipment, highly trained personnel, and provides high-quality service for every job.
FAQ
What are the main uses of CNC turning?
CNC turning is used to machine cylindrical parts, such as shafts, bushings, and rings. Many industries use this process to manufacture automotive parts, machine parts, and tools.
Can CNC turning process both metals and plastics?
Yes. CNC turning can process metals such as steel, iron, and aluminum, as well as plastics such as ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate.
How accurate is CNC turning?
CNC turning can achieve tolerances of ±0.005 inches (0.13 mm). This high precision helps in manufacturing parts that are dimensionally accurate and functionally sound.
What is the difference between CNC turning and CNC milling?
| Merkmal | CNC-Drehen | CNC-Fräsen |
|---|---|---|
| Part Movement | Spins the part | Moves the tool |
| Am besten für | Round shapes | Flat or complex shapes |
Why do companies choose Kaiming for CNC turning?
Kaiming utilizes advanced equipment and employs highly skilled workers. They conduct rigorous quality checks on every single part. Customers trust Kaiming because they provide durable, precise, and reliable parts.